Research Snapshots
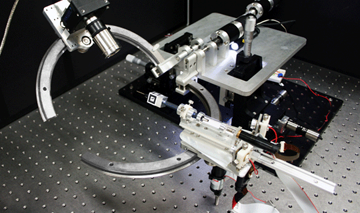
Intraocular Robotic Interventional and Surgical System
The IRISS is the result of research collaboration between the Mechatronics and Control Laboratory and the Jules Stein Eye Institute. The research vision is to develop a surgical platform capable of performing anterior and posterior surgical procedures via teleoperation and automation. The IRISS has the unique capability to manipulate two surgical instruments simultaneously through ocular incisions spaced millimeters apart. Read More »
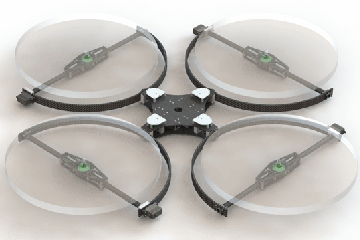
Airborne Manipulator with Twisting and Tilting Rotors for Omnidirectional Thrust Vectoring
In this project, we introduce a flying vehicle that overcomes the inherent maneuverability limitations of traditional multirotors. Full directional authority is enabled on each individual thrust vector by introducing two additional degrees of freedom (twist and tilt) to each rotor. The resulting system possesses omnidirectional thrust-vectoring capabilities, fully decouples the position and attitude dynamics, and minimizes wasted thrust over its entire configuration space. Read More »
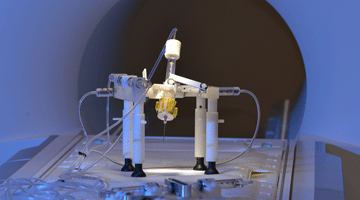
An MR-Compatible Motion Stage for Respiratory Motion Emulation
A collaboration between Maclab and Radiological Sciences, the MR Robot is a hydrostatically actuated robotic system for real-time MRI-guided interventions. Real-time image visualization and guidance are crucial for minimally invasive cancer interventions (e.g., prostate and abdomen). While the MRI provides excellent tissue contrast, multi-planar imaging, and non-ionizing energy, the closed bore limits physical access to the patient. For this reason, a MRI-compatabile robotic device is developed Read More »
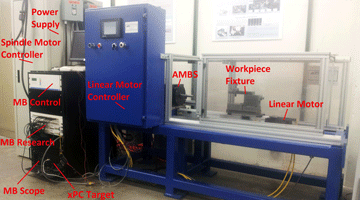
Active Magnetic Bearing Spindle System
The active magnetic bearing spindle system is based on the concept of a magnetically levitating shaft that allows the bearing to remain levitated and centered within its housing even when spinning and/or carrying a load. Modeling and control is carried out on the radial bearings with the thrust bearing stabilized by PID and the motor controlled by a commercial driver. Read More »
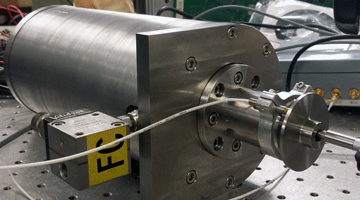
Fast Tool Servos for Precision Machining of Irregularly Shaped Surfaces
The fast tool servo (FTS) is a custom-designed tool holder used to cut piston pin holes. Piston pin holes have a unique non-circular geometry, they have an oval hole with a trumpet-shaped profile. This geometry is difficult to create because the work piece must remain stationary. The FTS mounts to a lathe and is designed to accept multiple sizes of boring bars. It uses a piezoelectric actuator to actuate the boring bar about a flexure. Read More »
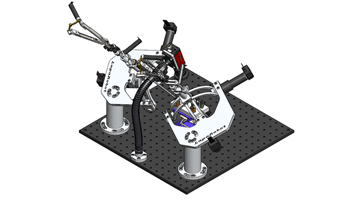
Telesurgical/Telementoring Laparoscopic Surgical Robot (LapaRobot)
The LapaRobot System is a 5 degree of freedom Master-Slave pair of robot manipulators that allows 2 users at different physical locations to perform interactive teaching (telementoring) and interactive learning in laparoscopic procedures, as well as cooperative telesurgery. In other words, the LapaRobot System allows less experienced or new surgeons to be taught and/or guided through laparoscopic procedures via a more experienced master surgeon. Read More »
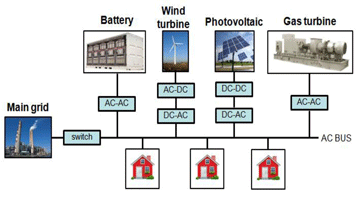
Hardware in the Loop Simulation and Control of Power Conversions in Smart Grid Operation
Smart Grids are system that contains at least one distributed energy resource (DER) and local loads. Every unit within the system exchanges information with each other so that smart grid can adapt to load changes and other influences. The challenges to the control of smart grid are: a) the control of each DER has to guarantee the output AC power is compatible with the grid. b) during transitions between grid-tied and off-grid mode. Read More »

Multi-Scale Alignment and Positioning System (MAPS)
Engineers in the NSF SINAM Center have designed and built a Multi-Scale Alignment and Positioning System (MAPS) for precision engineering. MAPS represents the culmination of 3 years work of an interdisciplinary and collaborative team. MAPS addresses a critical problem of industrial nanomanufacturing: how to scale production of nano-scale components with macroscopic scale tools. MAPS is currently a test-bed that provides 5 nm precision over distances of 2 inches. Read More »
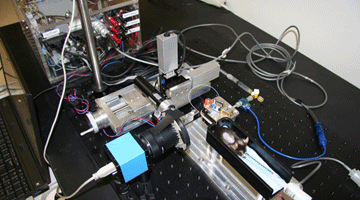
Mouse Tail Injection
Mouse tail injection studies the image-guided catheter injection control of the automated vascular injection, particularly for PET scans. The goal of this research is to develop a robust and efficient vein location estimation algorithm, and drive the catheter needle to perform chemical injection. Read More »

Magnetic Bearing
The MBC500 is a tabletop rotor system supported by electro-magnets rather than traditional journal bearings. Fitted with a turbine, the rotor can be spun up to high speeds to investigate various control stategies regarding the stabilization of a spinning rotor. Due to the actuator-sensor configuration, the MBC500 is also a good Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) testbed for controls research. Read More »

High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU)
HIFU utilizes intersecting beams of ultrasound waves to create a high intensity focal point. When the focus is located in soft tissue, the acoustic energy is absorbed and converted into heat. Beyond a certain threshold, this heat causes thermal coagulation of the tissue resulting in localized cell death. The key advantage of HIFU is that it is noninvasive. It does not require skin puncture and healthy tissue in the ultrasound near Þeld is left undamaged by the treatment. Read More »

Dual Stage Fast Tool Servo
This research involves the design and control of a Dual Stage Fast Tool Servo (FTS) for precision machining of complex non-circular shapes. A piezoelectric actuator of 20 microns motion is integrated with an existing electromagnetic linear actuator. Read More »

Air Hybrid Engine and Vehicle
This is a hybrid concept other than electric hybrid for vehicle fuel economy. Enabled by camless valvetrain, the engine is configured to run as a compressor during vehicle braking, thus vehicle kinetic energy is used to produce compressed air. Read More »
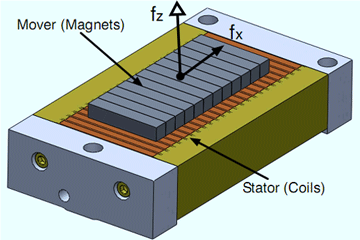
Linear Motor
Linear motors have been widely used in lithography, which are usually realized with optomechanical devices called a wafer scanner. Linear motors can provide both large travel range and precise motion. Nonlinear back lash and contact friction effects are also avoided with direct drive linear motors supported by air bearings or electromagnetic levitation. Read More »
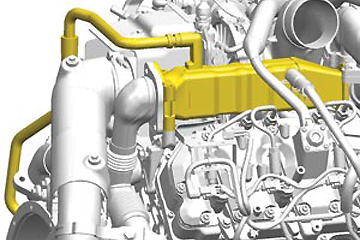
Waste Heat Recovery of Heavy-Duty Diesel Powertrain
Waste heat recovery in automotive vehicles is a method to extract energy as work that would otherwise be wasted through engine exhaust. The goal of this research is to model the Rankine power cycle in heavy-duty diesel powertrain and develop advanced control algorithms for optimal power generation and improved vehicle engine efficiency. Read More »
